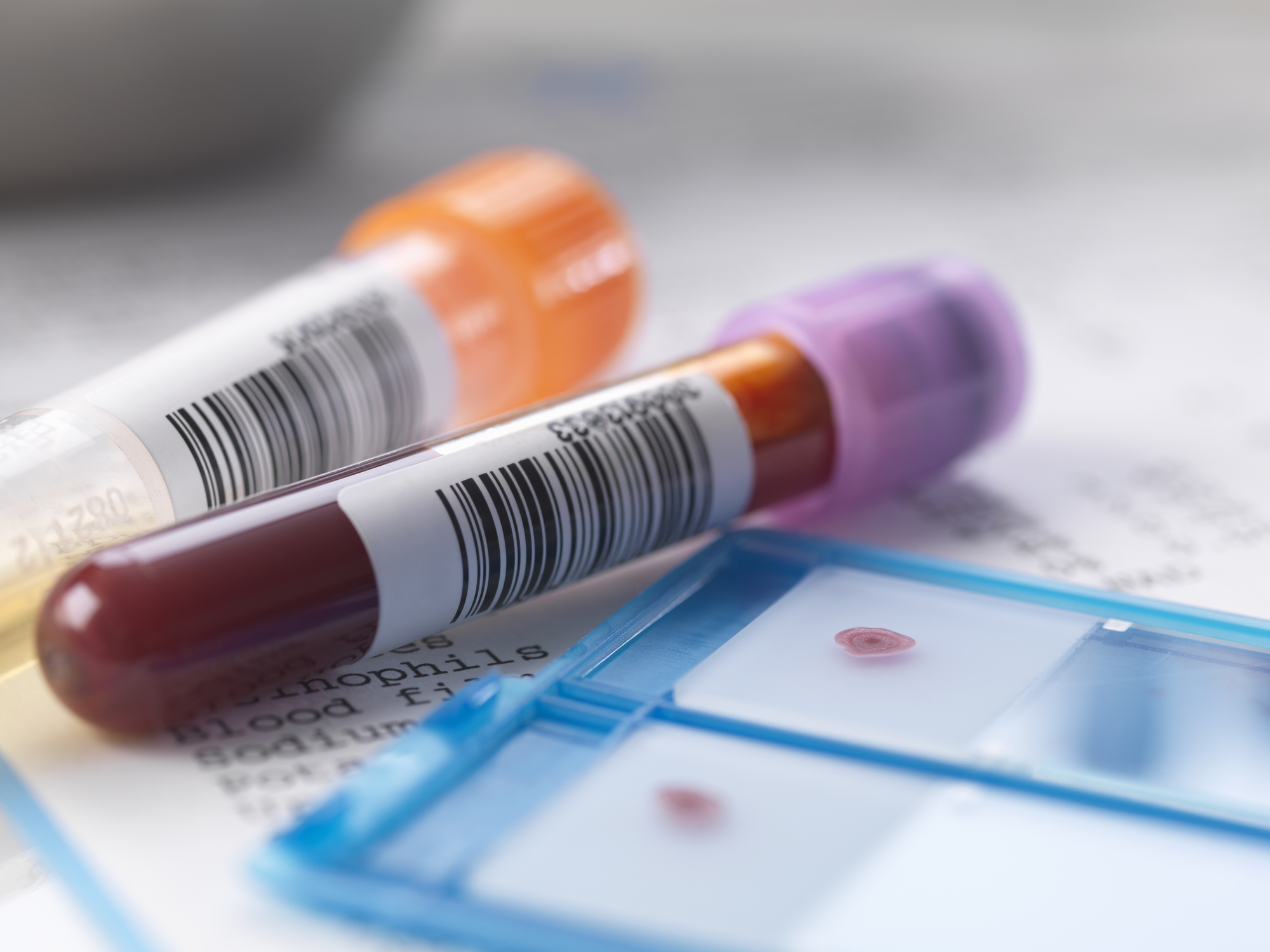
Haemoglobin is a type of protein contained in the red blood cells that transport oxygen from the lungs to all organs and carbon dioxide back to the lungs. Haemoglobin plays an important role in maintaining metabolism. The normal haemoglobin levels for adults are 13.5-17.5 g/dL for male and 12-15.5 g/dL for female.
To find out your haemoglobin levels, you’ll need to undergo a blood test. Low haemoglobin levels can be caused by anaemia or iron deficiency, pregnancy, liver or kidney problems, or chronic diseases. Overly high haemoglobin levels can be caused by smoking, bone marrow problems, dehydration, and use of drugs.
Low haemoglobin levels are always related to anaemia, due to their similar symptoms such as irregular heartbeat, pale skin and gum, fatigue, sudden bruises, and repeated headaches. However, some people with low haemoglobin levels do not experience specific symptoms or indication.
Overly high haemoglobin levels will also cause several symptoms, such as thicker blood, reddening face and feet, headache, stomachache, and haemorrhage. However, commonly overly high haemoglobin levels do not induce specific symptoms. Thus, regular health examination (including blood test) is needed to maintain your health and prevent diseases as early as possible.
Text by Anggie Triana
Stock photos from sbs.com.au
Source(s):
-
Hemoglobin, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMHT0022015/, 25 April 2018.
-
What’s to know about hemoglobin levels? (2017), https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/318050.php, 25 April 2018.
-
Symptoms of High Hemoglobin Levels (2018), https://india.curejoy.com/content/symptoms-of-high-hemoglobin-levels/, 25 April 2018.
-
High Hemoglobin Count (2018), https://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/high-hemoglobin-count/basics/causes/sym-20050862, 25 April 2018.